What is Earthing?
Equipment earthing is a connection done through a metal link between the body of any electrical appliance, or neutral point, as the case may be, to the deeper ground soil. The metal link is normally of MS flat, CI flat, GI wire which should be penetrated to the ground earth grid.
Equipment earthing is based on IS:3043-1987 Standards.
- Classification of electrical equipment IS: 9409-1980
- Important rules for safety and earthing practice is based on IE rules 1956
- Guide on effects of current passing through human body – IS:8437-1997
- Protection of buildings and structures from lightning – IS:2309-1969
- Earth: The conductive mass of the earth, whose electric potential at any point is conventionally assumed and taken as ZERO.
- Earth Electrode: A Conductor or group of conductors in intimate contact with and providing as electrical connection to earth.
- Earth Electrode Resistance: The electrical resistance of an earth electrode to the general mass of earth.
- Earthing Conductor: A protective conductor connecting the main earthing terminal to an earth electrode or other means of earthing.
- Equipotential Bonding: Electrical connection putting various exposed conductive parts and extraneous conductive parts at a substantially equal potential. Example: Inter connect protective conductor, earth continuity conductors and risers of AC/HV systems if any.
- Potential gradient: The potential difference per unit length measured in the direction in which it is max.
- Touch Voltage: The P.D. between a grounded metallic structure and a point on the earth’s surface separated by a horizontal reach of one Meter.
- Step Voltage: The P.D. between two points on the earth’s surface separated by a distance one pace (step) assumed to be one Meter.
- Earth Grid: A System of grounding electrodes consisting of interconnected connectors buried in the earth to provide a common ground from electrical devices and metallic structures.
- Earth Mat: A grounding system formed by a grid of horizontally buried conductors – Serves to dissipate the earth fault current to earth and also as an equipotential bonding conductor system.
Why Earthing is important
Earthing is important to ensure:
- Safety of personnel
- Safety of equipment
- Prevent or at least minimize damage to equipment as a result of flow of heavy currents
- Improvement of the reliability of the power system.
Classification of Earthing
The earthing is broadly divided as
- System earthing (Connection between part of plant in an operating system like LV neutral of a power transformer winding) and earth.
- Equipment earthing (safety grounding) connecting bodies of equipment (like electric motor body, transformer tank, switchgear box, operating rods of air break switches, LV breaker body, HV breaker body, feeder breaker bodies etc.) to earth.
Permissible Values of Earth Resistance
Reasonable values for earth resistance are:
- Power stations – 0.5 ohms
- EHT stations – 1.0 ohms
- 33KV SS – 2 ohms
- DTR structures – 5 ohms
- Tower foot resistance – 10 ohms
What is the Basics for Arriving at Permissible Earth Resistances?
As per IE rules one has to have a definite base for that as per IE rules one has to keep touch potential less than
- Recommended safe value 523 volts
- Ifault =maximum current in fault conditions
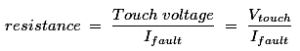
- Maximum fault current is 100 KVA the current in 100 KVA is about 100 A; where percentage
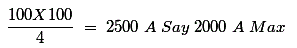
- For a substation of 100 KVA transformer
 0.26 ohms being quite low, quality work is to be done during construction, to obtain such a value of earthing system, and the expenditure for that will be very high.
0.26 ohms being quite low, quality work is to be done during construction, to obtain such a value of earthing system, and the expenditure for that will be very high.
Hence the electrical inspectors are insisting about 1.0 ohms. This seems justifying for the urban areas. This value may be 2 ohms in case of rural areas, which is recommended by most of the authorities. - The earth electrode resistance value also carries importance in view of full protection by lightning arrestors against lightning.
The earth electrode resistance value in that case is given by the formula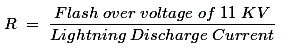 Flash over voltage of 11 KV = 75 KV, and a lightning arrestor Displacement = 40 KA.
Flash over voltage of 11 KV = 75 KV, and a lightning arrestor Displacement = 40 KA.
