The most complete Earth testers offer also earth resistivity measurement, which is defined as the resistance of the soil/ground shaped as a cube of 1 x 1 x 1 meter (1m3).
As we already explained, Soil resistance value depends on the nature of the soil and the percentage of water contained in it.
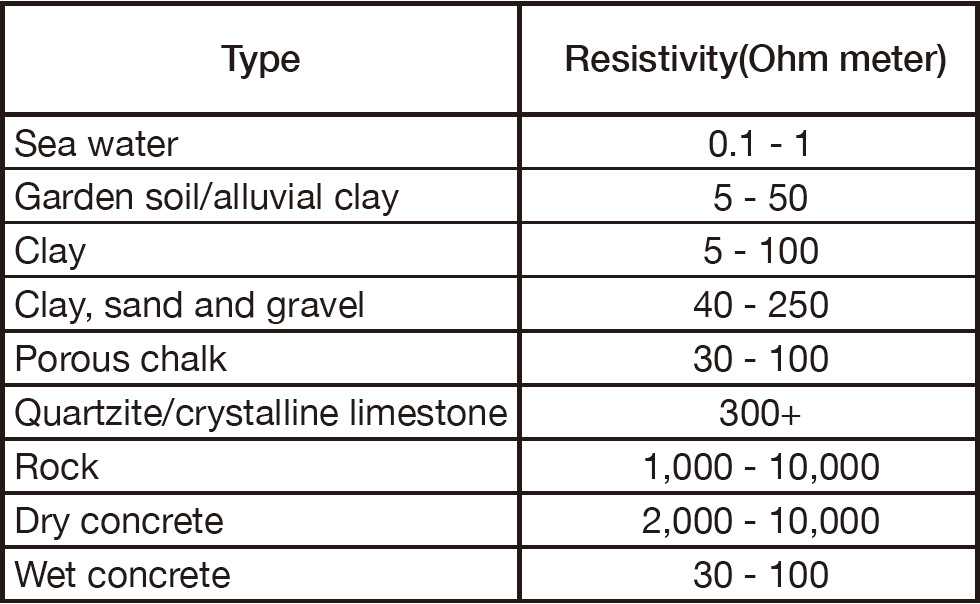
The below figure shows the values of earth resistivity for different soil types.
Soil resistance value depends on the nature of the soil and percentage of water contained.
The earth resistivity measurement is useful for soil surveys to establish the optimum design, depth and site location of earth electrode system. Such surveys are made, for example, when a new electrical generating station, substation, transmission tower, telecommunication station or tower is under construction. Without such surveys, extra cost of re-working electrode installations may be needed after the construction is finished.
The earth resistivity measurement may be used to indicate the degree of corrosion to be expected in underground pipelines for water, oil, gas, gasoline, etc. In general, corrosions tend to increase where there are spot areas with low resistivity values. This same kind of information is a good guide for installing cathodic protections for underground metallic pipelines.
Finally Earth resistivity measurements can be used conveniently for geophysical investigations.
For instance to locate minerals, clays, and water-bearing gravel beneath the earth’s surface, to determine depth to bed rock and thickness of glacial drift.
